Preventing cavities in toddlers and children is crucial for maintaining good oral health. Establishing good oral hygiene habits is the first step in cavity prevention, including regular brushing and flossing with fluoride toothpaste. Encouraging a healthy, balanced diet and limiting sugary and acidic foods and drinks can also help prevent cavities. Drinking plenty of water can help wash away food particles and bacteria and keep the mouth hydrated.
In addition to good oral hygiene habits and a healthy diet, regular dental checkups and cleanings are important for preventing cavities and other dental problems. Your pediatric dentist can detect and treat cavities early and recommend dental sealants to protect your child’s teeth from decay.
By following these tips and working closely with your pediatric dentist, you can help prevent cavities in toddlers and children and promote good oral health for life.
Dental sealants are thin coatings applied to the chewing surfaces of back teeth to prevent tooth decay. They work by filling in deep grooves and pits, making the surface easier to clean and less likely to trap bacteria and food particles.
Sealants can last for years and are checked during regular dental checkups. Using sealants as a preventative measure can help protect teeth from decay and promote good oral health.
|
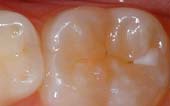
Before Sealant Applied
|
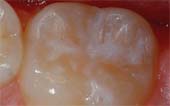
After Sealant Applied
|
Fluoride is important for maintaining good oral health in toddlers and children. It helps to strengthen tooth enamel, making teeth more resistant to decay.
It’s important to ensure your child gets the right amount of fluoride. Too little fluoride may not provide enough protection against decay. At the same time, too much fluoride can lead to dental fluorosis, which causes white spots or streaks on the teeth.
The American Dental Association recommends that children under three years old use a smear of fluoride toothpaste (about the size of a grain of rice) when brushing their teeth. Children between the ages of three and six should use a pea-sized amount of fluoride toothpaste.
 Mouth guards protect children’s teeth and jaws during physical activities and sports. Custom-fitted mouth guards made by a dentist provide the best fit and protection, but boil-and-bite mouth guards can be purchased at sporting goods stores.
Mouth guards protect children’s teeth and jaws during physical activities and sports. Custom-fitted mouth guards made by a dentist provide the best fit and protection, but boil-and-bite mouth guards can be purchased at sporting goods stores.
A well-fitted mouth guard should not interfere with breathing or speaking and should be worn during any activity that poses a risk of oral injury. Using a properly fitted mouth guard can help protect your child’s teeth and promote good oral health.
Xylitol is a natural sugar substitute that can help reduce cavities in children and adults. It works by inhibiting the growth of cavity-causing bacteria in the mouth, preventing them from producing harmful acids that erode tooth enamel.
Xylitol is found in many sugar-free gums, candies, and oral care products. It can be used as a natural sweetener in cooking and baking. Incorporating xylitol into your child’s diet and oral care routine can help reduce the risk of cavities and promote good oral health.
 Sports drinks are popular among children and teenagers but can pose hidden dangers to oral health. These drinks are often high in sugar and acid, eroding tooth enamel and increasing the risk of cavities.
Sports drinks are popular among children and teenagers but can pose hidden dangers to oral health. These drinks are often high in sugar and acid, eroding tooth enamel and increasing the risk of cavities.
In addition, frequent consumption of sports drinks can lead to tooth sensitivity and discoloration. It’s important to encourage your child to drink water instead of sports drinks and to limit their consumption of sugary and acidic foods and drinks for good oral health.
Here are some tips for consuming sports drinks in a way that minimizes the risk to oral health:
- Drink water before, during, and after physical activity to stay hydrated and avoid excessive consumption of sports drinks.
- Choose sports drinks with lower sugar and acid content, and drink them in moderation.
- Use a straw when drinking sports drinks to minimize contact with teeth.
- Rinse the mouth with water after drinking sports drinks to help neutralize acid and wash away sugar.
- Wait at least 30 minutes after drinking a sports drink before brushing your teeth, as brushing immediately after can cause further damage to tooth enamel.

